목차
예외처리 try{예외가 발생할 수 있는 구문}catch(잡아낼 클래스 변수){처리}
- 에러가 발생할 수 있는 상황을 회피하는 것
public class Ex01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
// if(b != 0) c = a / b;
try {
c = a / b;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){ // Exception이 발상하면 아래 코드 진행
c = 0;
}
System.out.println(a + "÷" + b + "=" + c );
}
}int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7};
try {
for(int i = 4; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("없는 인덱스");
}없는 인덱스int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7};
for(int i = 4; i >= 0; i--) {
try {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("없는 인덱스");
}
}없는 인덱스
7
5
3
1
- 다항성에 의해 부모 클래스를 갖는 Exception을 쓰면 더 많은 예외처리가 가능하다.
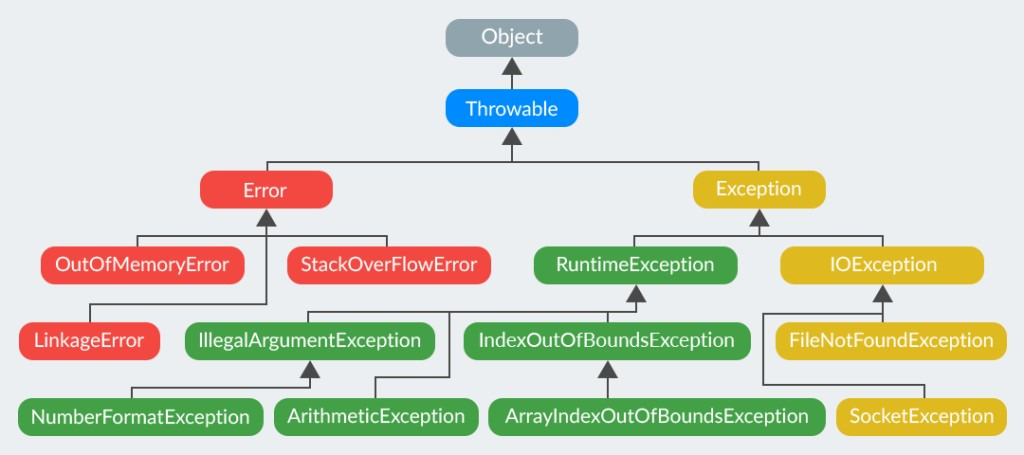
다중 catch 블럭
int[] arr = {-1, 0, 1, 2};
for(int i = 4; i >= 0; i--) {
try {
System.out.println(4 / arr[i]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("pass");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(0);
}
}에러메시지 출력하기
try {
int su = 1/ 0;
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e.getClass());
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}혹은
e.printStackTrace();=> 에러 메시지를 남겨놓는 코드는 시스템 자원에 여유가 있을 때 수행된다.
런타임 에러가 아닌 Exception 처리하기
Ex03 me = new Ex03();
try {
Object obj = me.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}public static void func01() {
try {
func02();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void func02() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
Ex03 me = new Ex03();
Object obj = me.clone();
}throw를 통한 예외처리
public class Ex03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
func01();
}
public static void func01() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
func02();
}
public static void func02() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
Ex03 me = new Ex03();
Object obj = me.clone();
System.out.println("test"); // 실행안됨
}
}finally
- 반드시 처리하는것을 목표로 한다.
int su = 0;
try {
int a = 1 / su;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("예외처리");
return;
}finally {
System.out.println("반드시 처리"); // 위 코드에 return이 있어도 수행되는 코드
}- catch()가 없어도 수행할 수 있다.(jdk 1.7~)
int su = 0;
try {
int a = 1 / su;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
}finally {
System.out.println("반드시 처리"); // 위 코드에 return이 있어도 수행되는 코드
}사용자 정의 Exception 만들기
class IdException extends Exception{
public IdException() {
super("존재하는 ID 입니다.");
}
}
public class Ex05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
func01();
} catch(IdException e) {
// System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void func01() throws IdException{
throw new IdException();
}
}I/O
File - 파일과 폴더(디렉토리)
public class Ex06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
java.io.File file;
// file = new File("ex01.txt");
// 상대경로
// file = new File("./ex01.txt");
file = new File("./src");
// 절대경로
// file = new File("C:\\workspace\\Day14\\ex01.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists()); // true
// 파일인지 디렉토리인지 확인
System.out.println("디렉토리 : " + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("파일 : " + file.isFile());
// 파일의 경로 확인
System.out.println(file.getPath());
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath()); // 항상 절대경로를 반환함
System.out.println("------------------------");
// 경로 따로 뽑기
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.getName());
// 읽기, 쓰기, 실행 권한
System.out.println(file.canRead());
System.out.println(file.canWrite());
System.out.println(file.canExecute());
// 파일의 사이즈 확인
System.out.println(file.length() + "byte");
// 파일이 마지막으로 수정된 시간
System.out.println(new java.util.Date(file.lastModified()));
// 디렉토리 안의 목록 보기
if(file.isDirectory()) {
String[] ex = file.list();
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(ex));
}
}존재하는 파일 지우기
public class Ex07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("ex01.txt");
if(f.exists()) {
boolean result = f.delete();
System.out.println("파일을 지웠습니다.");
}else {
System.out.println("파일이 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
}
}파일 만들기
public class Ex08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("ex01.txt");
if(f.exists()) {
System.out.println("파일이 존재합니다. ");
}else {
boolean result = f.createNewFile();
System.out.println("파일이 만들어졌습니다." + result);
}
}
}디렉토리 만들기
public class Ex09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// File f = new File("test1");
File f = new File("test1/ex02");
boolean result = f.mkdir();
if(result) System.out.println("디렉토리가 만들어 졌습니다.");
else System.out.println("디렉토리가 존재합니다.");
}
}디렉토리 지우기
public class Ex10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("test1/ex01"); // 디렉토리가 비어있어야 지울 수 있다.
boolean result = f.delete();
System.out.println(result);
}
}파일 쓰고 읽기
파일 쓰기
File f = new File("target02.txt");
try {
boolean result = f.createNewFile();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
////
String msg = "Hello World:D~~!!!!\n;D:D:D;D";
java.io.OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream(f);
for(int i = 0; i < msg.length(); i++) {
os.write(msg.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println("작성완료");
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(os != null) os.close();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}한글 쓰기
String msg = "한글 입력";
char[] arr = msg.toCharArray();
File f = new File("target02.txt");
////
java.io.OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream(f);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
os.write(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("작성완료");
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(os != null) os.close();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}파일 읽기
File f = new File("target02.txt");
java.io.InputStream is = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(f);
while(true) {
int su = is.read();
if(su == -1) break;
System.out.print((char)su);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(is != null) is.close();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}한글 읽기
File f = new File("target03.txt");
InputStream is = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[(int)f.length()];
try {
is = new FileInputStream(f);
int cnt = 0;
while(true) {
int su = is.read();
if(su == -1) break;
buf[cnt++] = (byte) su;
}
System.out.println(new String(buf));
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(is != null) is.close();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}파일 복사하기
File src = new File("image01.jpg");
File copy = new File("copy01.jpg");
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
copy.createNewFile();
is = new FileInputStream(src);
os = new FileOutputStream(copy);
int su = -1;
long before = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(true) {
su = is.read();
if(su == -1) break;
os.write(su);
}
long after = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("복사완료:" + (after - before) + "ms");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(os != null)os.close();
if(is != null)is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}문자열 stream (2byte 체계)
쓰기
File f = new File("test02.txt");
java.io.Writer fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(f);
fw.write('한');
fw.write('글');
fw.write(' ');
fw.write('지');
fw.write('원');
System.out.println("작성 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fw != null) fw.close();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}읽기
File f = new File("test02.txt");
Reader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(f);
while(true) {
int r = fr.read();
if(r == -1) break;
System.out.println((char)r);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fr != null) fr.close();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}'100일 챌린지 > 빅데이터기반 인공지능 융합 서비스 개발자' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Day 16 - Web(Tomcat 다운받기), html과 jsp (0) | 2024.08.12 |
|---|---|
| Day 15 - 새 창 띄우기, I/O에 버퍼 달기 (0) | 2024.08.09 |
| Day 13 - UI 구현하기 (0) | 2024.08.07 |
| Day12 - 내부 클래스, GUI (0) | 2024.08.06 |
| Day 11 - generic, 순서가 없는 자료구조(Enumeration),그리고 Map (0) | 2024.08.05 |